Every flood follows the laws of physics—but the damage it brings follows the laws of politics and economics. To understand Cebu’s recurring floods, we must examine not just rivers and drains, but land markets, incentives, and power structures.
A civic group recently released a petition calling for accountability. They demand institutional reforms and immediate interventions after the November 4, 2025 flooding. There is a deeper structural truth behind these recurrent failures—one that cannot be resolved through flood-control works alone. Flooding in Cebu is not simply a hydraulic engineering problem. It is a political economy problem. It is shaped by land markets and governance incentives. It also involves institutional weaknesses and the complex interactions between urban development and ecological systems.
The physical manifestations of Cebu’s flooding are evident. They include overflowing rivers, silted channels, blocked waterways, undersized drainage lines, and deteriorated uplands. These issues are symptoms of underlying drivers embedded in the way land is valued, used, occupied, and regulated. These systemic forces determine where people settle and where capital flows. They dictate how infrastructure is prioritized. They also influence which environmental limits are observed or ignored. Understanding the city’s flood crisis requires a new perspective. We must shift from short-term engineering responses. We should focus on a long-term examination of Cebu’s land governance and socio-economic structures.
The Limits of Engineering-Centered Solutions
For decades, Cebu’s response to flooding has relied on traditional engineering. This includes the expansion of drainage networks. It also involves the construction of embankments and the deepening of rivers. Additionally, there is the installation of floodwalls and diversion channels. These are necessary interventions and form part of any modern urban infrastructure system.
However, the severe flooding of November 4 demonstrated an important fact. Structural measures cannot compensate for degraded watersheds. They cannot make up for constricted waterways either. Additionally, land-use choices that contradict hydrological realities are not offset by these measures.
The core limitations are clear:
- Upstream forests have thinned, reducing water absorption.
- Urban surfaces have become more impermeable, rapidly increasing runoff.
- Natural retention areas have been converted into residential and commercial zones.
- Rivers have narrowed due to settlements, obstructions, and encroachments.
- Drainage systems designed for past rainfall patterns are now overwhelmed by climate-intensified storms.
Engineering solutions, however well-designed, cannot fully absorb the consequences of decades of unsustainable land use and misaligned development patterns.
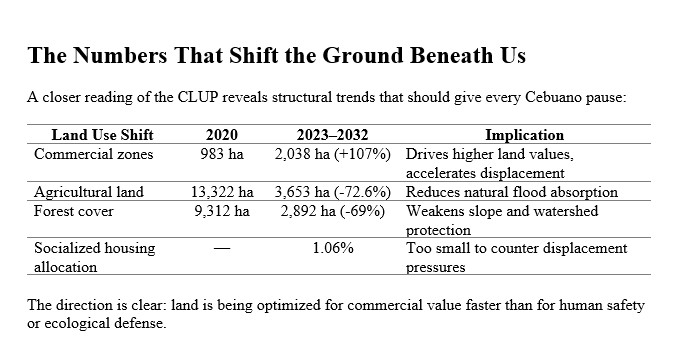
Land Market Pressures and Development in High-Risk Areas
Cebu’s flooding problem cannot be separated from the economics of land. As urban land becomes increasingly scarce and valuable, development pressures intensify toward hazard-prone areas:
- river easements and riparian buffers,
- wetlands and marshes,
- floodplains and low-lying coastal areas,
- steep upland slopes and watershed zones.
These areas historically served as natural drainage or water retention systems. Yet economic incentives—combined with regulatory concessions—have enabled their transformation into buildable parcels.
This trend reflects a market-driven logic: when prime land is limited, the pressure to develop environmentally sensitive areas becomes stronger. The result is a spatial configuration that maximizes short-term economic gains but increases long-term exposure to floods.
Thus, flooding is not merely caused by extreme rainfall. It is shaped by land scarcity and speculative development. Permissive regulatory environments also play a role in its formation. It is shaped by the interaction between land scarcity, speculative development, and permissive regulatory environments.
Political Incentives Favor Visible Infrastructure Over Preventive Governance
Flood-control infrastructures are politically compelling projects. They offer:
- highly visible outputs,
- significant budgets,
- recurring maintenance contracts,
- and narratives of action and responsiveness.
Because they are technically complex, such projects often escape broader public scrutiny. At the same time, some measures reduce long-term flood risk most effectively. These include watershed rehabilitation, strict easement enforcement, and climate-informed zoning. However, they are politically challenging. They require displacements, long-term planning consistency, and actions that may produce limited immediate political returns.
This imbalance in incentives explains why Cebu sees many flood-control structures. These structures do not always address the underlying drivers of vulnerability. Sometimes, they even worsen the situation.
Flooding persists not simply because engineering solutions are inadequate. It also occurs because political incentives prioritize short-term, highly visible outputs. These outputs are prioritized over structural preventive governance.
The issue is not a lack of technical knowledge among agencies. The problem continues because actions conflict with the interests of those who hold political and economic power.
This is the essence of the political economy argument.
River Degradation and Extractive Activities
Siltation, riverbed changes, and sediment buildup are major contributors to flood severity. These issues are exacerbated by:
- sand and gravel extraction,
- upland clearing for agriculture or development,
- informal excavation,
- and poor adherence to environmental safeguards.
These activities are sustained because they are economically profitable and often backed by political or economic influence. Despite their known impacts, they persist due to entrenched interests along the value chain—from local employment to construction demand.
Thus, river degradation is not merely a technical or enforcement issue. It is a governance challenge linked to resource extraction, revenue dependence, and regulatory gaps.
Enforcement Challenges Reflect Institutional Capture and Regulatory Asymmetry
Calls for strict enforcement frequently assume that institutions lack capacity or technical competence. In reality, enforcement failures are often tied to:
- local political alliances,
- informal settlements that represent vote-rich constituencies,
- economic actors with significant influence over land use decisions,
- fragmented authority across agencies,
- inconsistent application of zoning and environmental rules.
Hazard-prone areas become zones of negotiation rather than regulation. This institutional dynamic contributes to weak compliance, reinforcing land-use patterns that increase flood exposure.
Flooding, therefore, arises not only from natural or physical factors but also from institutional capture and uneven regulatory power.
From Flood Control to Flood Governance
The arguments focusing on removing obstructions, correcting flawed structures, or improving inter-agency coordination are important. Yet they must be integrated into a broader, structural framework of flood governance, one that recognizes the interconnectedness of:
- land markets,
- watershed systems,
- ecological integrity,
- urban density,
- climate projections,
- institutional frameworks,
- and political incentives.
A governance-centered approach requires:
- climate-sensitive and risk-informed land use planning,
- protection and restoration of watershed and riparian systems,
- strict implementation of easements and hazard-zone regulations,
- upstream retention strategies and nature-based solutions,
- green infrastructure that enhances urban permeability,
- basin-wide management across LGU boundaries,
- resilient zoning and development controls,
- and institutional reforms that shield planning from political and economic capture.
Cebu’s long-term resilience depends on integrating these elements into a coherent governance structure.
Conclusion
The November 4, 2025 flood event underscored the limitations of relying primarily on engineering-centric flood control. While structural interventions remain essential, they are insufficient against systemic land-use pressures. Institutional weaknesses and economic incentives drive risky development.
Flooding in Cebu is a political economy issue—rooted in how land is valued, governed, and contested. Meaningful solutions require a transition from reactive flood-control efforts. These solutions must embrace a comprehensive approach rooted in land governance, ecological integrity, institutional accountability, and long-term urban planning.
Cebu can only move toward true resilience through this shift. It will reduce its vulnerability to the increasingly severe impacts of climate and development pressures.